产品说明
Application
Water supply:Pressure boostingfor main pipes and high-rise buildings
Industrial pressure boosting: Water system,cleaning system,high pressure washing system and firefighting system
Pressure boosting for pressure tank,sprinkling irrigation and trichling irrigation Air conditioner,cooling system and industrial cleaning
Features
1.Economic vertical multistage pumps
2.Applicable for a wide scope of different termperatures, flow rates and pressure ranges
3.Water inlet and outlet can be rotatedfor proper assembly in accordance with installation requirement
4.Easy installation and maintenance
5.Advanced hydraulic model design,featuring stable operation and high efficiency
6.Cast iron water inlet and outlet with special anti-rust treatment
7.High-strength engineering plastic flow passage components
8.Reliable stainless steel welded shaft
Working Conditions
Liquid temperature:+5ºC~60ºC
Max.ambient temperature:+40ºC
Max.pressure:15bar
Altitude: up to 1000 m
Standard voltage: Single-phase:220~240V/50Hz
Three-phase:380~415v/50Hz
Accessories Parameters
| Part | Fan cover | Fan | Rear cover | Bearing | Stator | Rotor | Gasket | 法兰 | Motor bracket | Machanical seal | Machanical seal | Impeller | Diffuser | Last stage diffuser | Last stage diffuser |
| 材料 | 08F | 08F | Cast iron | Optional | Optional | Optional | Rubber | Cast iron | Aluminum | Ceramic/Carbor | AlSI 304 | Plastic | Plastic | Plastic | Plastic |
TECHNICAL DATA FOR EVP(m)2
| Single-phase | Three-phase | kW | HP | Q(1/min) | 0 | 16.7 | 33.3 | 50 | 66.7 |
| EVPm2-2 | EVP2-2 | 0.37 | 0.5 | (m) | 24 | 23 | 18 | 13 | 6 |
| EVPm2-3 | EVP2-3 | 0.55 | 0.75 | 36 | 33 | 26 | 20 | 9 | |
| EVPm2-4 | EVP2-4 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 48 | 45 | 35 | 26 | 11 | |
| EVPm2-5 | EVP2-5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 59 | 57 | 44 | 33 | 15 | |
| EVPm2-6 | EVP2-6 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 69 | 65 | 52 | 37 | 18 | |
| EVPm2-7 | EVP2-7 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 82 | 75 | 62 | 45 | 25 | |
| EVPm2-8 | EVP2-8 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 94 | 87 | 72 | 52 | 28 | |
| EVPm2-9 | EVP2-9 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 105 | 98 | 82 | 60 | 35 | |
| EVPm2-11 | EVP2-11 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 130 | 119 | 98 | 69 | 37 | |
| EVP2-13 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 153 | 142 | 115 | 80 | 39 |
TECHNICAL DATA FOR EVP(m)4
| 模型 | Power(P2) | Q(m³/h) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Single-phase | Three-phase | kW | HP | Q(1/min) | 0 | 16.7 | 33.3 | 50 | 66.7 | 83.3 | 100 |
| EVPm4-2 | EVP4-2 | 0.55 | 0.75 | (m) | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 18 | 15 | 10 |
| EVPm4-3 | EVP4-3 | 0.75 | 1.0 | 37 | 36 | 34 | 33 | 29 | 24 | 16 | |
| EVPm4-4 | EVP4-4 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 47 | 46 | 45 | 41 | 36 | 28 | 20 | |
| EVPm4-5 | EVP4-5 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 61 | 58 | 57 | 55 | 48 | 39 | 29 | |
| EVPm4-6 | EVP4-6 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 74 | 72 | 69 | 66 | 57 | 47 | 36 | |
| EVP4-7 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 86 | 83 | 81 | 77 | 68 | 57 | 43 | ||
| EVP4-8 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 98 | 95 | 92 | 86 | 76 | 63 | 47 | ||
| EVP4-10 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 116 | 114 | 110 | 102 | 90 | 73 | 57 | ||
| EVP4-12 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 145 | 142 | 140 | 131 | 115 | 97 | 75 | ||
TECHNICAL DATA FOR EVP(m)6
| 模型 | Power(P2) | Q(m³/h) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||
| Single-phase | Three-phase | kW | HP | Q(U/min) | 0 | 16.7 | 33.3 | 50 | 66.7 | 83.3 | 100 | 116.7 | 133.3 | 1510 | 166.7 |
| EVPm6-3 | EVP6-3 | 1.1 | 1.5 | (m) | 30 | 29.5 | 29 | 28.5 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 24.5 | 23 | 21 | 19 |
| EVPm6-4 | EVP6-4 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 40 | 38.5 | 37.5 | 37.3 | 37 | 36 | 34 | 33.5 | 32 | 30 | 27 | |
| EVP6-5 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 50 | 49 | 48.5 | 48.3 | 48 | 45 | 43 | 42 | 41 | 39 | 36 | ||
| — | .0EVP6-6 | 2.2 | 3.0 | 58 | 56 | 54 | 53.5 | 53 | 52 | 51 | 48 | 45 | 41 | 40 | |
| — | EVP6-7 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 68 | 67 | 66.5 | 65 | 63.5 | 62 | 60 | 58 | 56 | 54 | 51 | |
| EVP6-8 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 78 | 75 | 73 | 72 | 71 | 70 | 68 | 65 | 62 | 59 | 55 | ||
TECHNICAL DATA FOR EVP(m)6H
| 模型 | Power (P2) | Q (m³/h) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4.5 | 6 | 7.5 | 9 | 10.5 | ||
| Single-phase | Three-phase | kW | HP | Q (L/min) | 0 | 16.7 | 33.3 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 |
| EVPm6H-3 | EVP6H-3 | 1.1 | 1.5 | (m) | 39 | 38 | 37 | 35 | 33 | 29 | 24 | 18 | 10 |
| EVPm6H-4 | EVP6H-4 | 1.5 | 2 | 52 | 51 | 49 | 47 | 44 | 39 | 32 | 25 | 14 | |
| EVPm6H-5 | EVP6H-5 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 64 | 62 | 60 | 58 | 54 | 47 | 38 | 28 | 16 | |
| EVP6H-6 | 2.2 | 3 | 76 | 74 | 71 | 68 | 63 | 56 | 45 | 34 | 20 | ||
| — | EVP6H-8 | 3.0 | 4 | 103 | 100 | 97 | 95 | 90 | 80 | 66 | 50 | 31 | |
| — | EVP6H-10 | 4.0 | 5.5 | 130 | 127 | 124 | 121 | 114 | 103 | 86 | 66 | 41 | |
TECHNICAL DATA FOR EVP10H
| 模型 | Power (P2) | Q (m³/h) | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | |
| Three-phase | KW | HP | Q (L/min) | 0 | 33 | 67 | 100 | 133 | 167 | 200 | 233 | 267 |
| EVP10H-3 | 3.0 | 4.0 | H (m) |
56 | 55 | 54 | 52 | 49 | 46 | 42 | 39 | 29 |
| EVP10H-4 | 4.0 | 5.5 | 75 | 74 | 72 | 70 | 67 | 64 | 60 | 53 | 43 | |
| EVP10H-5 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 93 | 91 | 87 | 84 | 81 | 77 | 72 | 64 | 55 | |
| EVP10H-6 | 5.5 | 7.5 | 113 | 110 | 107 | 104 | 100 | 96 | 87 | 78 | 68 | |
| EVP10H-7 | 7.5 | 10 | 132 | 128 | 124 | 120 | 116 | 112 | 103 | 93 | 80 | |
| EVP10H-8 | 7.5 | 10 | 150 | 147 | 143 | 139 | 134 | 127 | 120 | 108 | 92 | |
FAQ:
Q: Do you supply sample? And leading time?
A:The sample can be sent to customer within 7-12 days. The batch order can be shipped within 35 days after receiving deposit payment.
Q:Where is your loading port?
A: HangZhou port, China
Q: Can you accept c ustomized products?
A: Yes we accept your specific order.
Q: What is your payment term?
A: 30% in advance, 70% balance the B/L or T/T.
Q: What is the warranty of the product?
A: We offer 1 year product life guarantee.
Q: What information shall I provide you when I need your offer?
A: Pump flow, total head, pump material (copper wire or aluminum wire? Stator length), voltage, frequency, etc.
Q: Will you supply any spare parts with the pumps?
A: Yes,Like tank, flexible hose, pressure switch, pressure gauge, brass connector, cable, etc.
Q: Is there any leakage problem of this pump?
A: Some factory may have such problem, but we solved it very well, by using good material of pump casing, O-ring, and they fit each other perfect. We use 8 screw on the pump head while others may use only 6 screw to save cost. We test 100% and long time for the pump head part, to make sure there is no leakage problem.
Q: Where did you export to?
A: We export to more than 50 countries, for example, Israel, South Africa, Germany, Poland, Spain, Vietnam, Malaysia, Russia, Thailand, Mexico, Brazil, Chile, etc.
Q: Can I order some accessories with the pump?
A: pressure tank, flexible hose, 5-way connector, pressure gauge, pressure controller and assemble
Q: Can the pump be made by customized voltage and frequency ?
A: Yes, 220-240V, 110V, 50Hz, 60Hz,,all OK!
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| 售后服务: | 1 年 |
|---|---|
| 保修: | 1 年 |
| Max.Head: | >150m |
| 样本 |
US$ 500/Piece
1 件(最小订单量) | 订购样品 |
|---|
| 定制: |
可用
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
运费:
每台设备的估计运费。 |
关于运费和预计交货时间。 |
|---|
| 付款方式: |
|
|---|---|
|
首次付款 全额付款 |
| 货币 | US$ |
|---|
| 退货与退款: | 您可以在收到产品后 30 天内申请退款。 |
|---|
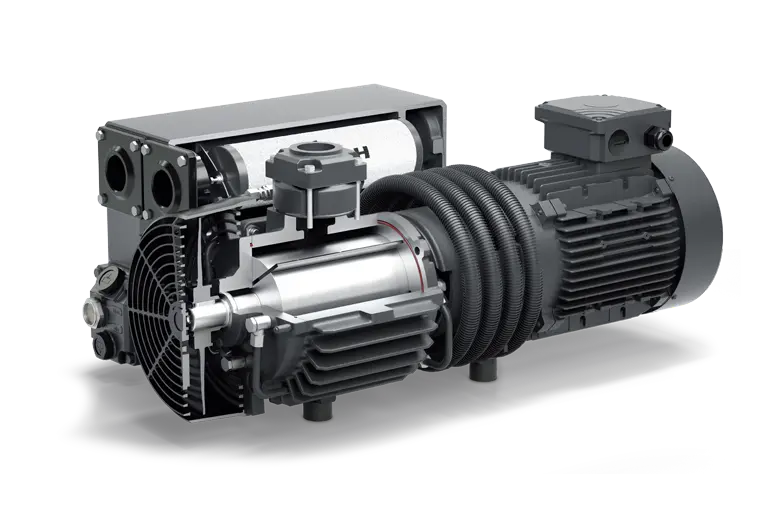
Can Vacuum Pumps Be Used in the Aerospace Sector?
Vacuum pumps indeed have various applications in the aerospace sector. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in several areas of the aerospace industry, supporting various processes and systems. Some of the key applications of vacuum pumps in the aerospace sector include:
1. Space Simulation Chambers: Vacuum pumps are used in space simulation chambers to replicate the low-pressure conditions experienced in outer space. These chambers are utilized for testing and validating the performance and functionality of aerospace components and systems under simulated space conditions. Vacuum pumps create and maintain the necessary vacuum environment within these chambers, allowing engineers and scientists to evaluate the behavior and response of aerospace equipment in space-like conditions.
2. Propellant Management: In space propulsion systems, vacuum pumps are employed for propellant management. They help in the transfer, circulation, and pressurization of propellants, such as liquid rocket fuels or cryogenic fluids, in both launch vehicles and spacecraft. Vacuum pumps assist in creating the required pressure differentials for propellant flow and control, ensuring efficient and reliable operation of propulsion systems.
3. Environmental Control Systems: Vacuum pumps are utilized in the environmental control systems of aircraft and spacecraft. These systems are responsible for maintaining the desired atmospheric conditions, including temperature, humidity, and cabin pressure, to ensure the comfort, safety, and well-being of crew members and passengers. Vacuum pumps are used to regulate and control the cabin pressure, facilitating the circulation of fresh air and maintaining the desired air quality within the aircraft or spacecraft.
4. Satellite Technology: Vacuum pumps find numerous applications in satellite technology. They are used in the fabrication and testing of satellite components, such as sensors, detectors, and electronic devices. Vacuum pumps help create the necessary vacuum conditions for thin film deposition, surface treatment, and testing processes, ensuring the performance and reliability of satellite equipment. Additionally, vacuum pumps are employed in satellite propulsion systems to manage propellants and provide thrust for orbital maneuvers.
5. Avionics and Instrumentation: Vacuum pumps are involved in the production and testing of avionics and instrumentation systems used in aerospace applications. They facilitate processes such as thin film deposition, vacuum encapsulation, and vacuum drying, ensuring the integrity and functionality of electronic components and circuitry. Vacuum pumps are also utilized in vacuum leak testing, where they help create a vacuum environment to detect and locate any leaks in aerospace systems and components.
6. High Altitude Testing: Vacuum pumps are used in high altitude testing facilities to simulate the low-pressure conditions encountered at high altitudes. These testing facilities are employed for evaluating the performance and functionality of aerospace equipment, such as engines, materials, and structures, under simulated high altitude conditions. Vacuum pumps create and control the required low-pressure environment, allowing engineers and researchers to assess the behavior and response of aerospace systems in high altitude scenarios.
7. Rocket Engine Testing: Vacuum pumps are crucial in rocket engine testing facilities. They are utilized to evacuate and maintain the vacuum conditions in engine test chambers or nozzles during rocket engine testing. By creating a vacuum environment, these pumps simulate the conditions experienced by rocket engines in the vacuum of space, enabling accurate testing and evaluation of engine performance, thrust levels, and efficiency.
It’s important to note that aerospace applications often require specialized vacuum pumps capable of meeting stringent requirements, such as high reliability, low outgassing, compatibility with propellants or cryogenic fluids, and resistance to extreme temperatures and pressures.
In summary, vacuum pumps are extensively used in the aerospace sector for a wide range of applications, including space simulation chambers, propellant management, environmental control systems, satellite technology, avionics and instrumentation, high altitude testing, and rocket engine testing. They contribute to the development, testing, and operation of aerospace equipment, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and safety.

What Is the Difference Between Dry and Wet Vacuum Pumps?
Dry and wet vacuum pumps are two distinct types of pumps that differ in their operating principles and applications. Here’s a detailed explanation of the differences between them:
Dry Vacuum Pumps:
Dry vacuum pumps operate without the use of any lubricating fluid or sealing water in the pumping chamber. They rely on non-contact mechanisms to create a vacuum. Some common types of dry vacuum pumps include:
1. Rotary Vane Pumps: Rotary vane pumps consist of a rotor with vanes that slide in and out of slots in the rotor. The rotation of the rotor creates chambers that expand and contract, allowing the gas to be pumped. The vanes and the housing are designed to create a seal, preventing gas from flowing back into the pump. Rotary vane pumps are commonly used in laboratories, medical applications, and industrial processes where a medium vacuum level is required.
2. Dry Screw Pumps: Dry screw pumps use two or more intermeshing screws to compress and transport gas. As the screws rotate, the gas is trapped between the threads and transported from the suction side to the discharge side. Dry screw pumps are known for their high pumping speeds, low noise levels, and ability to handle various gases. They are used in applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, chemical processing, and vacuum distillation.
3. Claw Pumps: Claw pumps use two rotors with claw-shaped lobes that rotate in opposite directions. The rotation creates a series of expanding and contracting chambers, enabling gas capture and pumping. Claw pumps are known for their oil-free operation, high pumping speeds, and suitability for handling dry and clean gases. They are commonly used in applications such as automotive manufacturing, food packaging, and environmental technology.
Wet Vacuum Pumps:
Wet vacuum pumps, also known as liquid ring pumps, operate by using a liquid, typically water, to create a seal and generate a vacuum. The liquid ring serves as both the sealing medium and the working fluid. Wet vacuum pumps are commonly used in applications where a higher level of vacuum is required or when handling corrosive gases. Some key features of wet vacuum pumps include:
1. Liquid Ring Pumps: Liquid ring pumps feature an impeller with blades that rotate eccentrically within a cylindrical casing. As the impeller rotates, the liquid forms a ring against the casing due to centrifugal force. The liquid ring creates a seal, and as the impeller spins, the volume of the gas chamber decreases, leading to the compression and discharge of gas. Liquid ring pumps are known for their ability to handle wet and corrosive gases, making them suitable for applications such as chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment.
2. Water Jet Pumps: Water jet pumps utilize a jet of high-velocity water to create a vacuum. The water jet entrains gases, and the mixture is then separated in a venturi section, where the water is recirculated, and the gases are discharged. Water jet pumps are commonly used in laboratories and applications where a moderate vacuum level is required.
The main differences between dry and wet vacuum pumps can be summarized as follows:
1. Operating Principle: Dry vacuum pumps operate without the need for any sealing fluid, while wet vacuum pumps utilize a liquid ring or water as a sealing and working medium.
2. Lubrication: Dry vacuum pumps do not require lubrication since there is no contact between moving parts, whereas wet vacuum pumps require the presence of a liquid for sealing and lubrication.
3. Applications: Dry vacuum pumps are suitable for applications where a medium vacuum level is required, and oil-free operation is desired. They are commonly used in laboratories, medical settings, and various industrial processes. Wet vacuum pumps, on the other hand, are used when a higher vacuum level is needed or when handling corrosive gases. They find applications in chemical processing, oil refining, and wastewater treatment, among others.
It’s important to note that the selection of a vacuum pump depends on specific requirements such as desired vacuum level, gas compatibility, operating conditions, and the nature of the application.
In summary, the primary distinction between dry and wet vacuum pumps lies in their operating principles, lubrication requirements, and applications. Dry vacuum pumps operate without any lubricating fluid, while wet vacuum pumps rely on a liquid ring or water for sealing and lubrication. The choice between dry and wet vacuum pumps depends on the specific needs of the application and the desired vacuum level.

什么是真空泵,它如何工作?
真空泵是一种机械设备,用于在封闭系统中创造和维持真空或低压环境。下面是详细的解释:
真空泵的工作原理是去除密封腔内的气体分子,降低腔内压力,从而形成真空。真空泵通过不同的机制和技术来实现这一目的,具体取决于真空泵的具体类型。以下是真空泵运行的基本步骤:
1.密封舱:
真空泵连接到一个密封的腔室或系统,需要从其中抽排空气或气体分子。真空室可以是容器、管道或任何其他封闭空间。
2.入口和出口:
真空泵有一个进气口和一个出气口。进气口与密封舱相连,而出气口可排入大气或与收集系统相连,以收集或释放抽空的气体。
3.机械动作:
真空泵产生一种机械作用,将气体分子从真空室中抽出。不同类型的真空泵采用不同的机制来实现这一目的:
- 正排量泵:这些泵通过物理方式捕获气体分子并将其从腔室中排出。例如旋片泵、活塞泵和隔膜泵。
- 动量传递泵:这类泵利用高速喷射或旋转叶片将动量传递给气体分子,将它们推出腔室。例如涡轮分子泵和扩散泵。
- 截留泵:这些泵通过将气体分子吸附或冷凝在表面或泵内材料中来捕获气体分子。低温泵和离子泵就是夹带泵的例子。
4.气体疏散:
真空泵工作时,会在腔室和泵之间产生压差。该压差会导致气体分子从真空室移动到泵的入口。
5.排气或收集:
一旦气体分子从腔室中排出,它们要么被排入大气,要么被收集起来并根据具体应用进行进一步处理。
6.压力控制:
真空泵通常包含压力控制机制,以保持腔体内所需的真空度。这些机制可包括阀门、调节器或反馈系统,用于调整泵的运行以达到所需的压力范围。
7.监测与安全:
真空泵系统可能包括传感器、压力表或指示器,用于监控压力水平、温度或其他参数。还可能包括泄压阀或联锁等安全功能,以保护系统和操作员免受超压或其他危险情况的影响。
需要注意的是,不同类型的真空泵可达到的真空度不同,适用于不同的压力范围和应用。真空泵的选择取决于所需的真空度、气体成分、抽气速度和具体应用要求等因素。
总之,真空泵是一种将气体分子从密封腔体中抽出,从而形成真空或低压环境的设备。真空泵通过正排量、动量传递或夹带等机械作用来实现这一目的。通过产生压差,真空泵将气体从腔室中抽出,气体被排出或收集。真空泵在包括制造、研究和科学应用在内的各行各业中发挥着至关重要的作用。


editor by CX 2023-12-23