Descrição do produto
High Head High Working Pressure Piston-Type Vacuum Pump for Electroplating
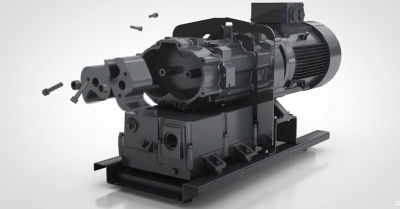
Product Introduction
The pump for the hydraulic double-cylinder double-acting ceramic plunger pump, combination with ceramic alumina plunger and sealing method.
Has a simple structure, stable operation, reliable performance, low noise and high working pressure, pressure fluctuations, small size, light weight, easy installation and maintenance, long life and other characteristics.
Descrição do produto
Dual-in and dual-out model
The double inlet and double outlet intelligent hydraulic plunger pump is a high-efficiency and energy-saving product developed by the company. The main wear-resistant components of this product have undergone special processing and have a long service life. At the same time, the cooling and lubrication circulating water has been
eliminated, greatly improving the working environment and achieving clean production. Compared to the series with the same flow rate and pressure, the power is reduced
by 40%. It is currently the most professional and efficient feed pump for filter presses. It can be widely used in wastewater treatment industries such as electroplating, printing and dyeing, chemical, municipal, mining, etc.
| Type | Rate flow rate(m3) | Pressure range(Mpa) | Rate pressure(Mpa) | Motor power(kw) | Inlet and outlet pipe diameter |
| ZP-D80 | 80 | 0~1.5 | 1.0 | 18.5 | DN125 |
| ZP-D120 | 120 | 0~1.5 | 1.0 | 30 | DN150 |
| ZP-D160 | 160 | 0~1.5 | 1.0 | 37 | DN150 |
| ZP-D200 | 200 | 0~1.5 | 1.0 | 45 | DN200 |
| ZP-D250 | 250 | 0~1.5 | 1.0 | 55 | DN200 |
Note: The above models are the basic models of plunger pumps, and our company can make various special products according to user requirements.
Our Advantages
Low noise, long service life, efficient and energy-saving, convenient maintenance, and low failure cost. (Compared to other similar products, the advantages are obvious.)
Application Range
Used for the coal washing industry
Used to print and dye leather municipal sewage treatment paper industry
Used for electroplating industry
Used for metal mining sand washing, river dredging industry
Used for the material transport industry
More Product
Packaging & Shipping
Payment
GLOYEL accept different kinds of payment,such as T/T, L/C, Western Union, Money Gram.
Shipment
GLOYEL has established long-term and reliable cooperation with professional packing and shipping company.
Recommended Product
| Serviço pós-venda: | Online Service |
|---|---|
| Garantia: | 1 ano |
| Estrutura: | Single Cylinder |
| Power: | Hydraulic |
| Application: | Slurry Treatment |
| Performance: | No Leak |
| Personalização: |
Disponível
|
|
|---|
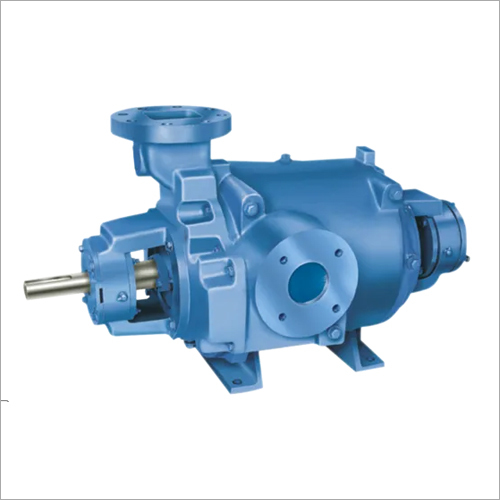

Qual é o impacto da altitude no desempenho da bomba de vácuo?
O desempenho das bombas de vácuo pode ser influenciado pela altitude em que elas são operadas. Aqui está uma explicação detalhada:
Altitude refere-se à elevação ou altura acima do nível do mar. À medida que a altitude aumenta, a pressão atmosférica diminui. Essa diminuição da pressão atmosférica pode ter vários efeitos sobre o desempenho das bombas de vácuo:
1. Redução da capacidade de sucção: As bombas de vácuo dependem do diferencial de pressão entre o lado da sucção e o lado da descarga para criar um vácuo. Em altitudes mais elevadas, onde a pressão atmosférica é menor, o diferencial de pressão disponível para a bomba trabalhar é reduzido. Isso pode resultar em uma diminuição da capacidade de sucção da bomba de vácuo, o que significa que ela pode não ser capaz de atingir o mesmo nível de vácuo que atingiria em altitudes mais baixas.
2. Nível de vácuo final mais baixo: O nível de vácuo máximo, que representa a pressão mais baixa que uma bomba de vácuo pode atingir, também é afetado pela altitude. Como a pressão atmosférica diminui com o aumento da altitude, o nível de vácuo máximo que pode ser atingido por uma bomba de vácuo é limitado. A bomba pode ter dificuldade para atingir o mesmo nível de vácuo que atingiria no nível do mar ou em altitudes mais baixas.
3. Velocidade de bombeamento: A velocidade de bombeamento é uma medida da rapidez com que uma bomba de vácuo pode remover gases de um sistema. Em altitudes mais elevadas, a pressão atmosférica reduzida pode levar a uma diminuição na velocidade de bombeamento. Isso significa que a bomba de vácuo pode levar mais tempo para evacuar uma câmara ou sistema até o nível de vácuo desejado.
4. Aumento do consumo de energia: Para compensar a diminuição do diferencial de pressão e atingir o nível de vácuo desejado, uma bomba de vácuo operando em altitudes mais elevadas pode exigir maior consumo de energia. A bomba precisa trabalhar mais para superar a pressão atmosférica mais baixa e manter a capacidade de sucção necessária. Esse aumento no consumo de energia pode afetar a eficiência energética e os custos operacionais.
5. Variações de eficiência e desempenho: Diferentes tipos de bombas de vácuo podem apresentar diferentes graus de sensibilidade à altitude. As bombas de palhetas rotativas vedadas a óleo, por exemplo, podem apresentar variações de desempenho mais significativas em comparação com as bombas secas ou outras tecnologias de bombas. O projeto e os princípios operacionais da bomba de vácuo podem influenciar sua capacidade de manter o desempenho em altitudes mais elevadas.
É importante observar que os fabricantes de bombas de vácuo normalmente fornecem especificações e curvas de desempenho para suas bombas com base em condições padronizadas, geralmente no nível do mar ou próximo a ele. Ao operar uma bomba de vácuo em altitudes mais elevadas, é aconselhável consultar as diretrizes do fabricante e considerar quaisquer limitações ou ajustes relacionados à altitude que possam ser necessários.
Em resumo, a altitude em que uma bomba de vácuo opera pode ter um impacto em seu desempenho. A pressão atmosférica reduzida em altitudes mais elevadas pode resultar na diminuição da capacidade de sucção, em níveis mais baixos de vácuo final, na redução da velocidade de bombeamento e no possível aumento do consumo de energia. Compreender esses efeitos é fundamental para selecionar e operar bombas de vácuo de forma eficaz em diferentes ambientes de altitude.
What Is the Role of Vacuum Pumps in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various aspects of pharmaceutical manufacturing. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Vacuum pumps are extensively used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to support a range of critical operations. Some of the key roles of vacuum pumps in pharmaceutical manufacturing include:
1. Drying and Evaporation: Vacuum pumps are employed in drying and evaporation processes within the pharmaceutical industry. They facilitate the removal of moisture or solvents from pharmaceutical products or intermediates. Vacuum drying chambers or evaporators utilize vacuum pumps to create low-pressure conditions, which lower the boiling points of liquids, allowing them to evaporate at lower temperatures. By applying vacuum, moisture or solvents can be efficiently removed from substances such as active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), granules, powders, or coatings, ensuring the desired product quality and stability.
2. Filtration and Filtrate Recovery: Vacuum pumps are used in filtration processes for the separation of solid-liquid mixtures. Vacuum filtration systems typically employ a filter medium, such as filter paper or membranes, to retain solids while allowing the liquid portion to pass through. By applying vacuum to the filtration apparatus, the liquid is drawn through the filter medium, leaving behind the solids. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient filtration, speeding up the process and improving product quality. Additionally, vacuum pumps can aid in filtrate recovery by collecting and transferring the filtrate for further processing or reuse.
3. Distillation and Purification: Vacuum pumps are essential in distillation and purification processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Distillation involves the separation of liquid mixtures based on their different boiling points. By creating a vacuum environment, vacuum pumps lower the boiling points of the components, allowing them to vaporize and separate more easily. This enables efficient separation and purification of pharmaceutical compounds, including the removal of impurities or the isolation of specific components. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various distillation setups, such as rotary evaporators or thin film evaporators, to achieve precise control over the distillation conditions.
4. Freeze Drying (Lyophilization): Vacuum pumps are integral to the freeze drying process, also known as lyophilization. Lyophilization is a dehydration technique that involves the removal of water or solvents from pharmaceutical products while preserving their structure and integrity. Vacuum pumps create a low-pressure environment in freeze drying chambers, allowing the frozen product to undergo sublimation. During sublimation, the frozen water or solvent directly transitions from the solid phase to the vapor phase, bypassing the liquid phase. Vacuum pumps facilitate efficient and controlled sublimation, leading to the production of stable, shelf-stable pharmaceutical products with extended shelf life.
5. Tablet and Capsule Manufacturing: Vacuum pumps are utilized in tablet and capsule manufacturing processes. They are involved in the creation of vacuum within tablet presses or capsule filling machines. By applying vacuum, the air is removed from the die cavity or capsule cavity, allowing for the precise filling of powders or granules. Vacuum pumps contribute to the production of uniform and well-formed tablets or capsules by ensuring accurate dosing and minimizing air entrapment, which can affect the final product quality.
6. Sterilization and Decontamination: Vacuum pumps are employed in sterilization and decontamination processes within the pharmaceutical industry. Autoclaves and sterilizers utilize vacuum pumps to create a vacuum environment before introducing steam or chemical sterilants. By removing air or gases from the chamber, vacuum pumps assist in achieving effective sterilization or decontamination by enhancing the penetration and distribution of sterilants. Vacuum pumps also aid in the removal of sterilants and residues after the sterilization process is complete.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps, such as rotary vane pumps, dry screw pumps, or liquid ring pumps, may be utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing depending on the specific requirements of the process and the compatibility with pharmaceutical products.
In summary, vacuum pumps play a vital role in various stages of pharmaceutical manufacturing, including drying and evaporation, filtration and filtrate recovery, distillation and purification, freeze drying (lyophilization), tablet and capsule manufacturing, as well as sterilization and decontamination. By enabling efficient and controlled processes, vacuum pumps contribute to the production of high-quality pharmaceutical products, ensuring the desired characteristics, stability, and safety.
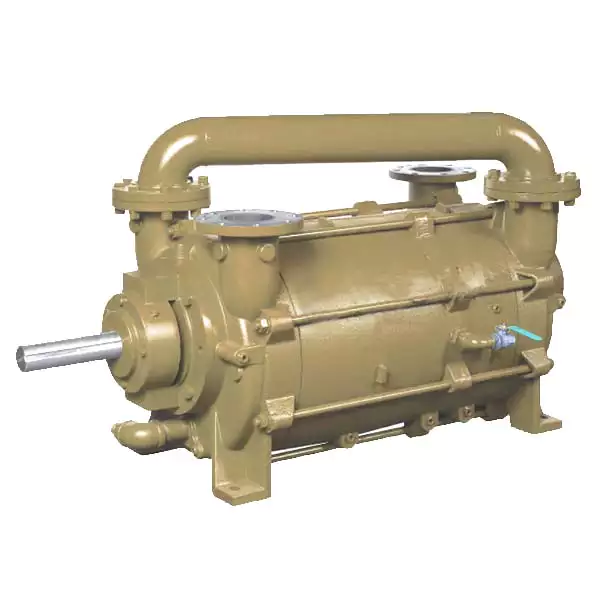

What Is a Vacuum Pump, and How Does It Work?
A vacuum pump is a mechanical device used to create and maintain a vacuum or low-pressure environment within a closed system. Here’s a detailed explanation:
A vacuum pump operates on the principle of removing gas molecules from a sealed chamber, reducing the pressure inside the chamber to create a vacuum. The pump accomplishes this through various mechanisms and techniques, depending on the specific type of vacuum pump. Here are the basic steps involved in the operation of a vacuum pump:
1. Sealed Chamber:
The vacuum pump is connected to a sealed chamber or system from which air or gas molecules need to be evacuated. The chamber can be a container, a pipeline, or any other enclosed space.
2. Inlet and Outlet:
The vacuum pump has an inlet and an outlet. The inlet is connected to the sealed chamber, while the outlet may be vented to the atmosphere or connected to a collection system to capture or release the evacuated gas.
3. Mechanical Action:
The vacuum pump creates a mechanical action that removes gas molecules from the chamber. Different types of vacuum pumps use various mechanisms for this purpose:
– Positive Displacement Pumps: These pumps physically trap gas molecules and remove them from the chamber. Examples include rotary vane pumps, piston pumps, and diaphragm pumps.
– Momentum Transfer Pumps: These pumps use high-speed jets or rotating blades to transfer momentum to gas molecules, pushing them out of the chamber. Examples include turbomolecular pumps and diffusion pumps.
– Entrapment Pumps: These pumps capture gas molecules by adsorbing or condensing them on surfaces or in materials within the pump. Cryogenic pumps and ion pumps are examples of entrainment pumps.
4. Gas Evacuation:
As the vacuum pump operates, it creates a pressure differential between the chamber and the pump. This pressure differential causes gas molecules to move from the chamber to the pump’s inlet.
5. Exhaust or Collection:
Once the gas molecules are removed from the chamber, they are either exhausted into the atmosphere or collected and processed further, depending on the specific application.
6. Pressure Control:
Vacuum pumps often incorporate pressure control mechanisms to maintain the desired level of vacuum within the chamber. These mechanisms can include valves, regulators, or feedback systems that adjust the pump’s operation to achieve the desired pressure range.
7. Monitoring and Safety:
Vacuum pump systems may include sensors, gauges, or indicators to monitor the pressure levels, temperature, or other parameters. Safety features such as pressure relief valves or interlocks may also be included to protect the system and operators from overpressure or other hazardous conditions.
It’s important to note that different types of vacuum pumps have varying levels of vacuum they can achieve and are suitable for different pressure ranges and applications. The choice of vacuum pump depends on factors such as the required vacuum level, gas composition, pumping speed, and the specific application’s requirements.
In summary, a vacuum pump is a device that removes gas molecules from a sealed chamber, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. The pump accomplishes this through mechanical actions, such as positive displacement, momentum transfer, or entrapment. By creating a pressure differential, the pump evacuates gas from the chamber, and the gas is either exhausted or collected. Vacuum pumps play a crucial role in various industries, including manufacturing, research, and scientific applications.


editor by CX 2023-12-01