Descripción del producto
Recommends Products
| DCVS Central Vacuum System | SMVS Micro-Vacuum System | DPSB Silent Dry Screw Vacuum Pump |
| DPSE Water Cooled Dry Screw Vacuum Pump | SV CHINAMFG Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump | RSS Roots Screw Vacuum System |
Descripción del producto
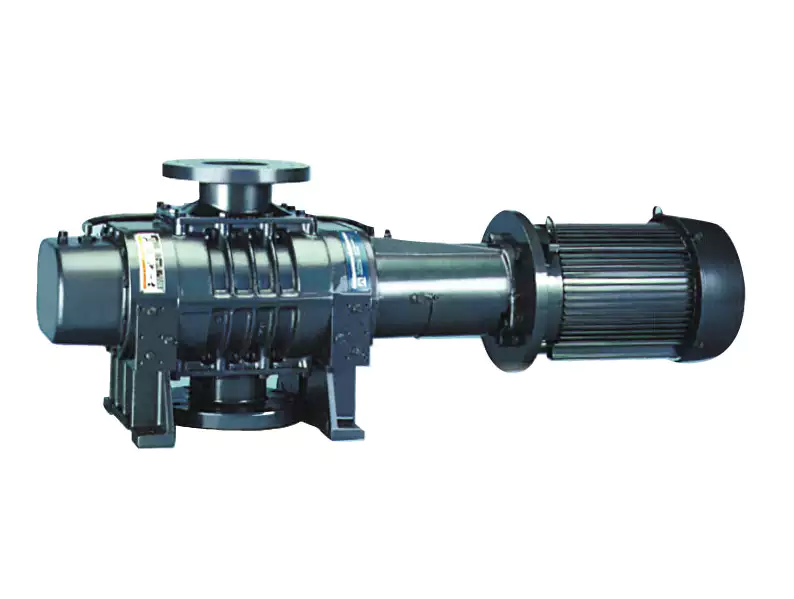
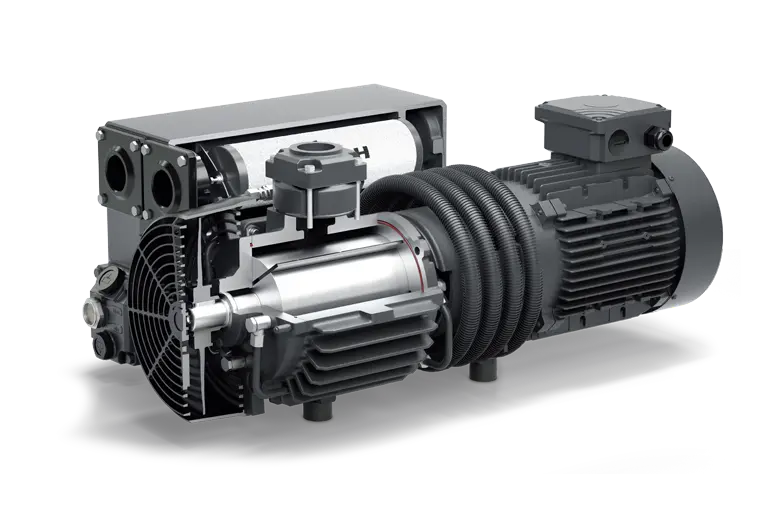
CHINAMFG Air Cooled Dry Screw Vacuum Pump:
DPS dry compound screw vacuum pump is the innovation and development of AfaPa’s products, using the fifth generation of compound variable pitch screw technology (30% energy saving, low exhaust temperature), with high efficiency, energy saving, environmental protection, lightweight, easy operation, reliable performance characteristics. It will be main developing trend of the vacuum pump in future.
Working Principle:
Dry compound screw vacuum pump are consist of 2 paralleled screw rotors and pump body form multiple sealed space, rotor and rotor, rotor and pump body all keep minuscule clearance(no touch, no friction), with the reverse gears driving, gas keep continuously transfer from inlet hole to outlet hole. Due to 2 rotors and pump body have no friction each other, need not lubrication oil, can keep clean gas. Gas keep continuously transfer, short passageway, high efficiency, outlet hole position lower than screw rotors, strong drainage ability, easy to clean, no intermediate bulkhead(claw vacuum pump and rotors vacuum pump have intermediate bulkhead), better exhaust and drainage, easy to maintain.
Our Advantages
1. Air cooled design.
2. Working chamber 100% no oil.
3. Strong resistance to water vapor.
4. Newest variable pitch screw rotors.
5. No contact double screw rotors.
6. Self-design multistage flat seal.
7. Max vacuum reach at 1Pa.
Parámetros del producto
| Modelo | DPS571 | DPS050 | DPS080 |
| Pumping Speed(m3/h) | 20 | 50 | 80 |
| Max Vacuum(Pa/Torr) | <3/0.02 | ||
| Motor Power(Kw/Hp) | 1.1/1.5 | 1.5/2.0 | 2.2/3.0 |
| Rotaring Speed(RPM) | 2980 | ||
| Working Voltage(V/HZ/Phase) | 220-480 / 50/60 / 3 | ||
| Structure | Horizontal Type | ||
| Inlet Hole | KF25 | KF40 | KF40 |
| Outlet Hole | KF25 | KF25 | KF25 |
| Cooling Method | Air Cooled | ||
| Sealing Method | Mechanical Flat Seal | ||
| Gear/Bearing Lubrication | 100# Synthetic Gear Oil | ||
| Noise(dB) | 65 | 70 | 72 |
| Peso (Kg) | 42 | 56 | 64 |
| Dimension(LxWxH, MM) | 669x303x258 | 769x330x292 | 850x330x292 |
| Remark: 1m3/h=0.2778L/S, 1m3/h=0.5883CFM. 1Pa=0.01mbar, 1Pa=0.001Kpa, 1Pa=0.0075Torr, 1Pa=0.000145PSI, 1Pa=0.00001Bar. |
|||
Embalaje y envío
Exhibition
Project Case
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
Q1: If I want to inquiry, what can I need to offer?
A1: Please tell us your Working Vacuum Degree(Pa,mbar or torr), Flowrate(L/S or M3/H) and Usage.
Q2: Do you have MOQ?
A2: 1Pcs is ok,if you have more quantity, the price will be cut down.
Q3: How long to delivery?
A3: We need about 4-5 weeks to produce,then extra need about 5-7 days to arrange domestic delivery and port clearence.
Q4: What is your payment term?
A4: 50% for prepayment, then the balance should paid before delivery, by TT.
Q5: How long for the warranty?
A5: 1 year for whole machine, the effective date of warranty should be counted from 1 month the goods arrived in client’s site. If the pump go wrong, the client can choose back the pump to factory repair,or we offer remote technical support.
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Servicio postventa: | Remote Support |
|---|---|
| Garantía: | 1 año |
| Oil or Not: | Oil Free |
| Personalización: |
Disponible
|
|
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Gastos de envío:
Flete estimado por unidad. |
sobre los gastos de envío y el plazo de entrega estimado. |
|---|
| Forma de pago: |
|
|---|---|
|
Pago inicial Pago completo |
| Moneda: | US$ |
|---|
| Devoluciones: | Puede solicitar el reembolso hasta 30 días después de recibir los productos. |
|---|

What Is the Role of Vacuum Pumps in Semiconductor Manufacturing?
Vacuum pumps play a critical role in semiconductor manufacturing processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
Semiconductor manufacturing involves the production of integrated circuits (ICs) and other semiconductor devices used in various electronic applications. Vacuum pumps are used extensively throughout the semiconductor manufacturing process to create and maintain the required vacuum conditions for specific manufacturing steps.
Here are some key roles of vacuum pumps in semiconductor manufacturing:
1. Deposition Processes: Vacuum pumps are used in deposition processes such as physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD). These processes involve depositing thin films of materials onto semiconductor wafers to create various layers and patterns. Vacuum pumps help create a low-pressure environment necessary for precise control of the deposition process, ensuring uniform and high-quality film formation.
2. Etching and Cleaning: Vacuum pumps are utilized in etching and cleaning processes, which involve the removal of specific layers or contaminants from semiconductor wafers. Dry etching techniques, such as plasma etching and reactive ion etching, require a vacuum environment to facilitate the ionization and removal of material. Vacuum pumps aid in creating the necessary low-pressure conditions for efficient etching and cleaning processes.
3. Ion Implantation: Ion implantation is a process used to introduce impurities into specific regions of a semiconductor wafer to modify its electrical properties. Vacuum pumps are used to evacuate the ion implantation chamber, creating the required vacuum environment for accurate and controlled ion beam acceleration and implantation.
4. Wafer Handling and Transfer: Vacuum pumps are employed in wafer handling and transfer systems. These systems utilize vacuum suction to securely hold and manipulate semiconductor wafers during various manufacturing steps, such as loading and unloading from process chambers, robotic transfer between tools, and wafer alignment.
5. Load Lock Systems: Load lock systems are used to transfer semiconductor wafers between atmospheric conditions and the vacuum environment of process chambers. Vacuum pumps are integral components of load lock systems, creating and maintaining the vacuum conditions necessary for wafer transfer while minimizing contamination risks.
6. Metrology and Inspection: Vacuum pumps are utilized in metrology and inspection tools used for characterizing semiconductor devices. These tools, such as scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) and focused ion beam (FIB) systems, often operate in a vacuum environment to enable high-resolution imaging and accurate analysis of semiconductor structures and defects.
7. Leak Detection: Vacuum pumps are employed in leak detection systems to identify and locate leaks in vacuum chambers, process lines, and other components. These systems rely on vacuum pumps to evacuate the system and then monitor for any pressure rise, indicating the presence of leaks.
8. Cleanroom Environment Control: Semiconductor manufacturing facilities maintain cleanroom environments to prevent contamination during the fabrication process. Vacuum pumps are used in the design and operation of the cleanroom ventilation and filtration systems, helping to maintain the required air cleanliness levels by removing particulates and maintaining controlled air pressure differentials.
Vacuum pumps used in semiconductor manufacturing processes are often specialized to meet the stringent requirements of the industry. They need to provide high vacuum levels, precise control, low contamination levels, and reliability for continuous operation.
Overall, vacuum pumps are indispensable in semiconductor manufacturing, enabling the creation of the necessary vacuum conditions for various processes, ensuring the production of high-quality semiconductor devices.
How Do Vacuum Pumps Impact the Quality of 3D Printing?
Vacuum pumps play a significant role in improving the quality and performance of 3D printing processes. Here’s a detailed explanation:
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by depositing successive layers of material. Vacuum pumps are utilized in various aspects of 3D printing to enhance the overall quality, accuracy, and reliability of printed parts. Here are some key ways in which vacuum pumps impact 3D printing:
1. Material Handling and Filtration: Vacuum pumps are used in 3D printing systems to handle and control the flow of materials. They create the necessary suction force to transport powdered materials, such as polymers or metal powders, from storage containers to the printing chamber. Vacuum systems also assist in filtering and removing unwanted particles or impurities from the material, ensuring the purity and consistency of the feedstock. This helps to prevent clogging or contamination issues during the printing process.
2. Build Plate Adhesion: Proper adhesion of the printed object to the build plate is crucial for achieving dimensional accuracy and preventing warping or detachment during the printing process. Vacuum pumps are employed to create a vacuum environment or suction force that securely holds the build plate and ensures firm adhesion between the first layer of the printed object and the build surface. This promotes stability and minimizes the risk of layer shifting or deformation during the printing process.
3. Material Drying: Many 3D printing materials, such as filament or powdered polymers, can absorb moisture from the surrounding environment. Moisture-contaminated materials can lead to poor print quality, reduced mechanical properties, or defects in the printed parts. Vacuum pumps with integrated drying capabilities can be employed to create a low-pressure environment, effectively removing moisture from the materials before they are used in the printing process. This ensures the dryness and quality of the materials, resulting in improved print outcomes.
4. Resin Handling in Stereolithography (SLA): In SLA 3D printing, a liquid resin is selectively cured using light sources to create the desired object. Vacuum pumps are utilized to facilitate the resin handling process. They can be employed to degas or remove air bubbles from the liquid resin, ensuring a smooth and bubble-free flow during material dispensing. This helps to prevent defects and imperfections caused by trapped air or bubbles in the final printed part.
5. Enclosure Pressure Control: Some 3D printing processes, such as selective laser sintering (SLS) or binder jetting, require the printing chamber to be maintained at a specific pressure or controlled atmosphere. Vacuum pumps are used to create a controlled low-pressure or vacuum environment within the printing chamber, enabling precise pressure regulation and maintaining the desired conditions for optimal printing results. This control over the printing environment helps to prevent oxidation, improve material flow, and enhance the quality and consistency of printed parts.
6. Post-Processing and Cleaning: Vacuum pumps can also aid in post-processing steps and cleaning of 3D printed parts. For instance, in processes like support material removal or surface finishing, vacuum systems can assist in the removal of residual support structures or excess powder from printed objects. They can also be employed in vacuum-based cleaning methods, such as vapor smoothing, to achieve smoother surface finishes and enhance the aesthetics of the printed parts.
7. System Maintenance and Filtration: Vacuum pumps used in 3D printing systems require regular maintenance and proper filtration to ensure their efficient and reliable operation. Effective filtration systems within the vacuum pumps help to remove any contaminants or particles generated during printing, preventing their circulation and potential deposition on the printed parts. This helps to maintain the cleanliness of the printing environment and minimize the risk of defects or impurities in the final printed objects.
In summary, vacuum pumps have a significant impact on the quality of 3D printing. They contribute to material handling and filtration, build plate adhesion, material drying, resin handling in SLA, enclosure pressure control, post-processing and cleaning, as well as system maintenance and filtration. By utilizing vacuum pumps in these critical areas, 3D printing processes can achieve improved accuracy, dimensional stability, material quality, and overall print quality.

How Are Vacuum Pumps Different from Air Compressors?
Vacuum pumps and air compressors are both mechanical devices used to manipulate air and gas, but they serve opposite purposes. Here’s a detailed explanation of their differences:
1. Function:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps are designed to remove or reduce the pressure within a closed system, creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. They extract air or gas from a chamber, creating suction or negative pressure.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors, on the other hand, are used to increase the pressure of air or gas. They take in ambient air or gas and compress it, resulting in higher pressure and a compacted volume of air or gas.
2. Pressure Range:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps are capable of generating pressures below atmospheric pressure or absolute zero pressure. The pressure range typically extends into the negative range, expressed in units such as torr or pascal.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors, on the contrary, operate in the positive pressure range. They increase the pressure above atmospheric pressure, typically measured in units like pounds per square inch (psi) or bar.
3. Applications:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps have various applications where the creation of a vacuum or low-pressure environment is required. They are used in processes such as vacuum distillation, vacuum drying, vacuum packaging, and vacuum filtration. They are also essential in scientific research, semiconductor manufacturing, medical suction devices, and many other industries.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors find applications where compressed air or gas at high pressure is needed. They are used in pneumatic tools, manufacturing processes, air conditioning systems, power generation, and inflating tires. Compressed air is versatile and can be employed in numerous industrial and commercial applications.
4. Design and Mechanism:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps are designed to create a vacuum by removing air or gas from a closed system. They may use mechanisms such as positive displacement, entrapment, or momentum transfer to achieve the desired vacuum level. Examples of vacuum pump types include rotary vane pumps, diaphragm pumps, and diffusion pumps.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors are engineered to compress air or gas, increasing its pressure and decreasing its volume. They use mechanisms like reciprocating pistons, rotary screws, or centrifugal force to compress the air or gas. Common types of air compressors include reciprocating compressors, rotary screw compressors, and centrifugal compressors.
5. Direction of Air/Gas Flow:
– Vacuum Pumps: Vacuum pumps draw air or gas into the pump and then expel it from the system, creating a vacuum within the chamber or system being evacuated.
– Air Compressors: Air compressors take in ambient air or gas and compress it, increasing its pressure and storing it in a tank or delivering it directly to the desired application.
While vacuum pumps and air compressors have different functions and operate under distinct pressure ranges, they are both vital in various industries and applications. Vacuum pumps create and maintain a vacuum or low-pressure environment, while air compressors compress air or gas to higher pressures for different uses and processes.


editor by CX 2024-02-16